Communication Ports
Imprivata uses a variety of TCP and UDP ports in its communications. The following describes the use of these ports to enable firewall administrators to configure rules that will allow these communications to take place.
Diagrammatic Summary
The following image represents the Imprivata communication port summary.
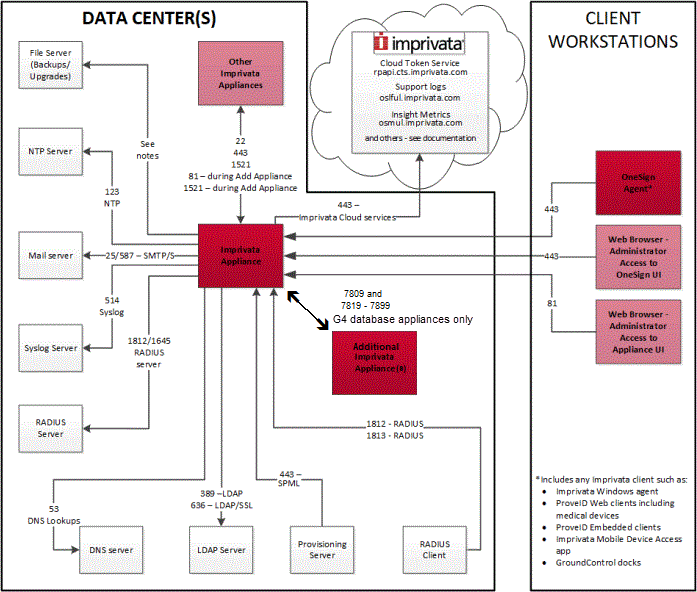
For additional information on outbound communication ports, including detailed information on Imprivata cloud services, see About Outbound Communications.
Appliance and Agent Operations
The following ports are used for the administration of Imprivata appliances, communication between two or more Imprivata appliances, or communication between an Imprivata appliance and an Imprivata agent.
| Port | Protocol | Direction | Description |
|
443 |
TCP | Inbound |
This port is used:
|
| 81 | TCP | Inbound | This port is used for Imprivata Appliance Console access. In addition this port must be open from a new appliance to the authorizing appliance when running the installation wizard on a new appliance. |
| 22 | TCP | Two-way | Secured via SSH and normally only open to the specific appliance IP addresses of other appliances in the enterprise. |
| 1521 | TCP | Two-way | Secured using Oracle encryption and only open to the specific appliance IP addresses of other appliances in the enterprise. It is used outgoing only for physical access systems. |
The ICMP (Internet Control Message Protocol) control message types in the next table are used to support ping tests between appliances. Note that these are not TCP or UDP ports.
| ICMP Control Message Type | Protocol | Description | Use by Imprivata Appliances |
|
ICMP Type 0 |
ICMP |
Echo Reply |
These allow ping tests to occur between appliances to test for the presence of a remote appliance. |
| ICMP Type 8 | ICMP | Echo Request | |
| ICMP Type 42 | ICMP | Extended Echo Request | |
| ICMP Type 43 | ICMP | Extended Echo Reply |
Cisco Adaptive Security Appliances with Application Layer Protocol Inspection: SQLnet inspection impedes communication between the Imprivata server and the database when the Imprivata server connects to a database on a remote appliance. This can occur during a database restore operation, an upgrade operation, and during a synchronize enterprise database operation. According to the Cisco Security Appliance Command Reference, version 8.0: Disable SQL*Net inspection when SQL data transfer occurs on the same port as the SQL control TCP port 1521. The security appliance acts as a proxy and reduces the client window size from 65,000 to about 16,000, causing data transfer issues.
Also, from the Oracle Support site: It is not just Cisco firewalls that can suffer from these problems. A common cause is the firewall's "Advanced SQL features" with various wording (depending on the vendor): SQLNet fixup (protocol), Deep Packet Inspection or DPI, SQLNet packet inspection, or SQL ALG (Juniper firewalls). Therefore, regardless of firewall vendor, you should disable the “Advanced SQL features” when present on your firewall(s).
G4 Database Appliance Communications
For Imprivata G4 (fourth generation) database appliances (but not for G4 service appliances), in addition to the ports listed in the previous section, the following ports are used:
| Ports | Protocol | Direction | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
|
7809 |
TCP | Two-way | This port is used only for communication between database appliances and is secured using encryption. |
| 7819 through 7899 | TCP | Two-way | These ports are used only for communication between database appliances and are secured using encryption. |
LDAP Server Ports
These ports must be open on the LDAP server:
| Port | Protocol | Direction | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
|
389 |
TCP | Outbound | This port is used for non-encrypted communication with the LDAP server |
| 636 | TCP | Outbound | This port is used for SSL communication with the LDAP server. |
Network Integration
These ports must be open on the DNS and NTP servers.
| Port | Protocol | Direction | Description |
|
53 |
TCP or UDP | Outbound | To the DNS server for lookups of addresses that need to be resolved. |
| 123 | TCP or UDP | Outbound | To an NTP server. |
Backups and Upgrades
An Imprivata appliance can be configured to communicate with a file server for the purposes of backing up the appliance to a secure location, or the storage of upgrade media for upload to the appliance at a convenient time. The file server can be an FTP server, a Microsoft Share or an SCP server.
| Port | Protocol | Direction | Description |
|
FTP |
TCP | Outbound |
Allows FTP operations in both Active and Passive mode:
|
| MS Share | TCP | Outbound | Consult Microsoft documentation for a summary of the port numbers required. |
| SCP | TCP | Outbound | Secure Copy uses SSH (port 22) to communicate with the Secure Server. |
Logging and Alerts
The Imprivata server can send SMTP alerts via a designated mail server, and can also integrate with a Syslog server.
| Port | Protocol | Direction | Description |
| 25 | TCP | Outbound | To the mail server using the SMTP protocol. |
| 514 | UDP | Outbound | Used for communication to syslog server. |
RADIUS Server Integration
The following ports are utilized when integrating with RADIUS.
| Port | Protocol | Direction | Description |
| 1812 | UDP | Inbound | If you are using RADIUS host or Proxy feature, these ports are open on the appliance inbound. The ports only accept RADIUS connections in this case. |
| 1813 | UDP | Inbound | |
| 1812 or 1645 | UDP | Outbound | Connections to an external RADIUS server such as an RSA RADIUS server. The request is outbound to the RSA Server that is listening on port 1812 or port 1645. |
Microsoft Remote PC RDP Automation
The following ports are utilized with Remote PC RDP automation.
| Port | Protocol | Direction |
| 135 | TCP | Two-way |
| 49666 | TCP | Two-way |